Charm metadata
The only file that must be present in a charm is metadata.yaml, in the root
directory. A metadata file must be a valid yaml dictionary, containing at least
the following fields:
nameis the charm name, which is used to form the charm URL.- It can only contain
a-z,0-9, and-; must start witha-z; must not end with a-; and may only end with digits if the digits are not directly preceded by a space. Stick with names likefooandfoo-bar-bazand you needn't pay further attention to the restrictions.
- It can only contain
summaryis a one-line description of the charm.descriptionis a long-form description of the charm and its features. It will also appear in the juju GUI.tagsis a descriptive tag that is used to sort the charm in the store.
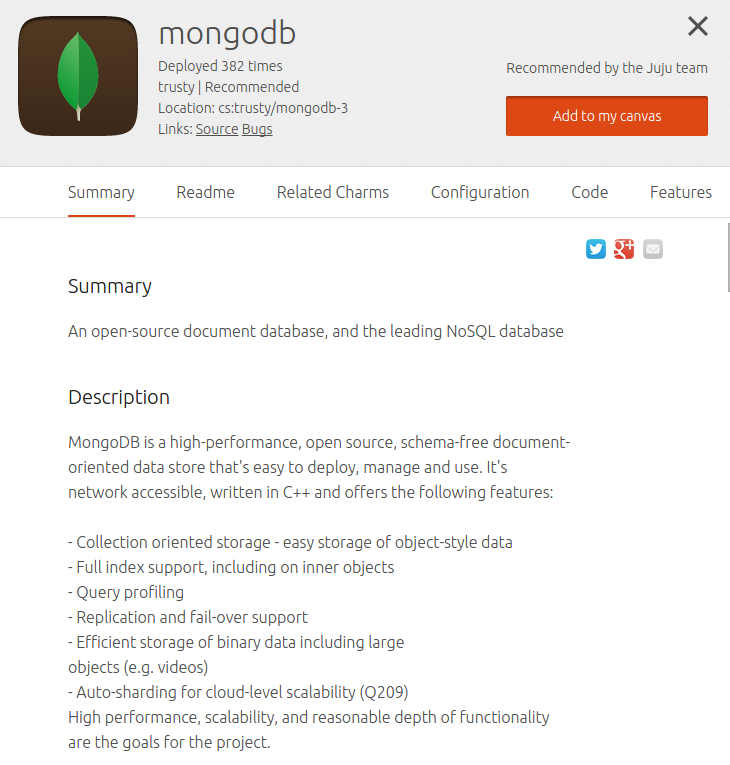
Here's a valid metadata file:
name: mongodb
summary: An open-source document database, and the leading NoSQL database
description: |
MongoDB is a high-performance, open source, schema-free document- oriented
data store that's easy to deploy, manage and use. It's network accessible,
written in C++ and offers the following features:
- Collection oriented storage
- easy storage of object-style data
- Full index support, including on inner objects
- Query profiling
- Replication and fail-over support
- Efficient storage of binary data including large objects (e.g. videos)
- Auto-sharding for cloud-level scalability (Q209) High performance,
scalability, and reasonable depth of functionality are the goals for the
project.
With only those fields, a metadata file is valid, but not very useful. Charms for use in the Charm Store should always set the following fields as well, for categorization and display in the GUI:
-
maintaineris the name and email address for the main point of contact for the development and maintenance of the charm. The maintainer field should be in the formatCharm Author Name <author@email>. -
maintainersis a list of people who maintain the charm. Use the yaml sequence format when there are more than one person maintaining the project. -
tagsis a list containing one or more of the following:- analytics
- big_data
- ecommerce
- openstack
- cloudfoundry
- cms
- social
- streaming
- wiki
- ops
- backup
- identity
- monitoring
- performance
- audits
- security
- network
- storage
- database
- cache-proxy
- application_development
- web_server
In almost all cases, only one tag will be appropriate. The categories help keep the Charm Store organised.
min-juju-versionCharms can declare the minimum Juju version the code is compatible with. This is useful when the code uses features introduced in a specific version of Juju. When supplied this value is the lowest version of Juju controller that will run the charm.
Storage
Storage can also be declared in a charm's metadata, as such:
storage:
data:
type: filesystem
description: junk storage
shared: false # not yet supported, see description below
read-only: false # not yet supported, see description below
minimum-size: 100M
location: /srv/data
A metadata file defines the charm's relations, and whether it's designed for deployment as a subordinate service.
subordinateshould be set to true if the charm is a subordinate. If omitted, the charm will be presumed not to be subordinate.provides,requires, andpeersdefine the various relations the charm will participate in.- if the charm is subordinate, it must contain at least one
requiresrelation with container scope.
Resources
resources allows you to add blobs that your charm can utilize.
resources:
example:
type: file # "file" is the only type supported currently
filename: example.tar.gz
description: example resource
Payloads
Payloads provide a means for the charm author to get information from a deployed charm. This is especially useful in large and complex deployments. For instance, the author may want to check the status of some element of the deployment such as a Docker container.
Payloads are defined in the payloads section of metadata.yaml by assigning
a class and type. A class defines the name of the payload and the type
describes the nature of the payload. Both are author-defined and are not
validated by Juju.
The most common types of payload are based on Docker, KVM, and LXD.
As an example, below, the following class/type pairs are defined: 'monitoring/docker', 'kvm- guest/kvm', and 'lxd-container/lxd':
payloads:
monitoring:
type: docker
kvm-guest:
type: kvm
lxd-container:
type: lxd
Payloads can be viewed using juju list-payloads and managed from the charm hook using the following commands:
- payload-register
- payload-unregister
- payload-status-set
See the Hook tools documentation for further details on these payload commands.
Extra-bindings
extra-bindings represents an extra bindable endpoint that is not used with
relations. These are useful when you want to have Juju provide distinct
addresses for an application on one or more spaces. For example, adding this
section to a YAML file for an application called "foo":
extra-bindings:
cluster:
public:
Will permit you to deploy the charm using --bind to deploy on units that have
access to the "admin-api", "public-api", and "internal-api" spaces with a'
different network interface and address for each binding, using this:
juju deploy ~/path/to/charm/foo --bind "cluster=admin-api public=public-api internal-api"
And running network-get cluster --primary-address will return only the
address coming from the "admin-api" space.
Endpoint names are strings and must not match existing relation names from the Provides, Requires, or Peers metadata sections. The values beside each endpoint name must be left out (i.e. "foo": <anything> is invalid).
Other available fields are:
seriesis a list of series that the charm supports.- It can include code names of Ubuntu releases such as 'trusty' or 'xenial'.
- It can also include code names for non-Ubuntu series such as 'centos7'.
termslists the terms the user must agree to before using the charm.min-juju-versionthe minimum version of Juju this charm is compatible with.
Other field names should be considered to be reserved; please don't use any not listed above to avoid issues with future versions of Juju.